Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

PBT D01
MI: 7-15 g/10min
(Custom materials available according to your Technical Data Sheet)
- Product Details
-
Download

Customizable Materials Available:
- Color (Customization of plastic pellet color according to your requirements.)
- Flame retardant grade (Let us know which flame retardant level you need: 0.8mm-3.0mm HB, V0, V1, V2, 5VA, 5VB)
- Glass fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- Carbon fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- UV resistance property (Tell us the application scenarios or UV resistance level of the materials.)
- Other materials can also be customized (Just need to provide your Technical Data Sheet.)
Technical Data Sheet of PBT D01
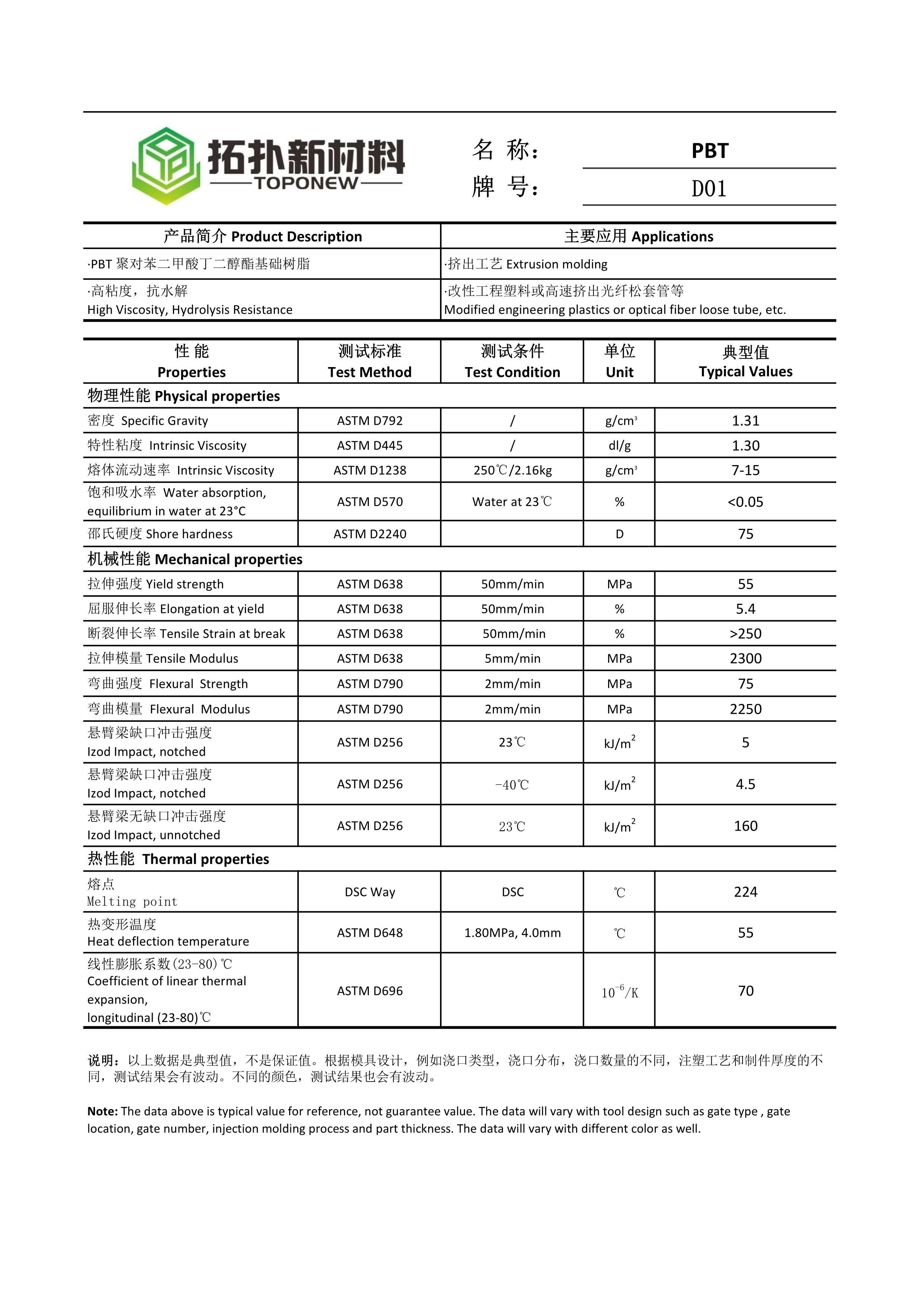
Properties of PBT D01
1.High Viscosity: PBT boasts high viscosity, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring precise molding or extrusion processes. Its exceptional flow characteristics contribute to the production of smooth and uniform fiber optic cables, ensuring optimal performance.
2.Low Carboxyl End-Group Content: With low carboxyl end-group content, PBT exhibits enhanced chemical stability. This property significantly contributes to the long-term performance and durability of fiber optic components. By minimizing the potential for degradation, PBT helps maintain superior signal transmission quality.
3.Hydrolysis Resistance: One of the notable advantages of PBT is its excellent resistance to hydrolysis. Fiber optic cables often come in contact with moisture due to various environmental factors. PBT's inherent ability to withstand hydrolytic degradation ensures the longevity and reliability of fiber optic applications, even in challenging conditions.
4.Ideal for Modified Engineering Plastics: Apart from its suitability for fiber optic loose tubes, PBT serves as an excellent base resin for modified engineering plastics. Its versatility allows for easy customization and modification to meet specific application requirements. By using PBT as a base resin, manufacturers can enhance the mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties of the final product.
Compare PBT pellets (Polybutylene terephthalate) and ABS pellets (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Composition: PBT is a thermoplastic polyester, while ABS is a thermoplastic polymer blend.
Properties: PBT pellets have good electrical insulating properties, high strength, and chemical resistance. ABS pellets, on the other hand, offer good impact resistance, rigidity, and heat resistance.
Processing: PBT pellets have a high melt viscosity, making them suitable for injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. ABS pellets also have good processing characteristics and can be easily molded using injection molding or extrusion methods.
Applications: PBT pellets are commonly used in electrical and electronics industries for connectors, switches, and insulators. ABS pellets find applications in automotive parts, toys, consumer goods, and appliances.
Appearance: PBT pellets are typically opaque and have a smooth surface. ABS pellets are also opaque but can have a glossy or textured surface.
Cost: The cost of PBT and ABS pellets may vary depending on factors such as availability, market demand, and specific grades. Generally, ABS pellets tend to be more affordable compared to PBT pellets.
Overall, both PBT and ABS pellets have their unique properties and applications. The choice between them would depend on the specific requirements of the desired end product.
Related Product:
https://www.toponew.com/products/abs-compound/ABS-A010208-16
PBT stands for Polybutylene Terephthalate, which is a type of thermoplastic polyester resin. The basic composition of PBT includes:
-
Polymer Backbone: The main component of PBT is the polymer chains made up of repeating units of butylene terephthalate. These chains provide PBT with its structural integrity and properties.
-
Butylene Units (C4H8O2): The butylene units are derived from 1,4-butanediol, which contributes to the flexibility and toughness of the polymer structure.
-
Terephthalate Units (C8H6O4): The terephthalate units are derived from terephthalic acid, providing rigidity, strength, and thermal stability to the polymer.
-
Additives: PBT resins may also contain additives such as reinforcing fibers (e.g., glass fibers), fillers, stabilizers, flame retardants, and lubricants to enhance specific properties or to aid in processing.
PBT is known for its excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. It is commonly used in various industries for applications such as automotive components, electrical and electronics parts, appliances, and consumer goods.
Download
-
PBT D01.pdf
Download PBT D01.pdf









