Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

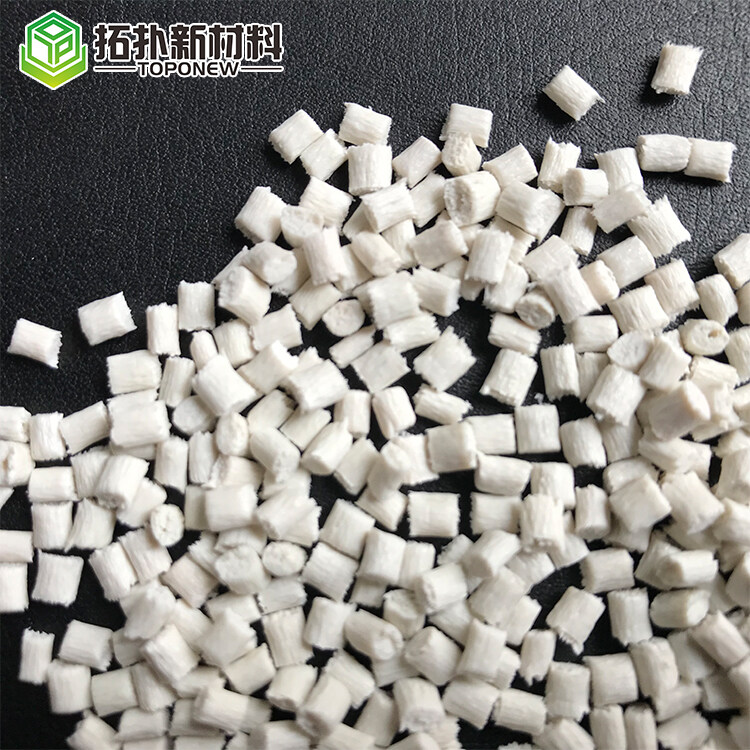
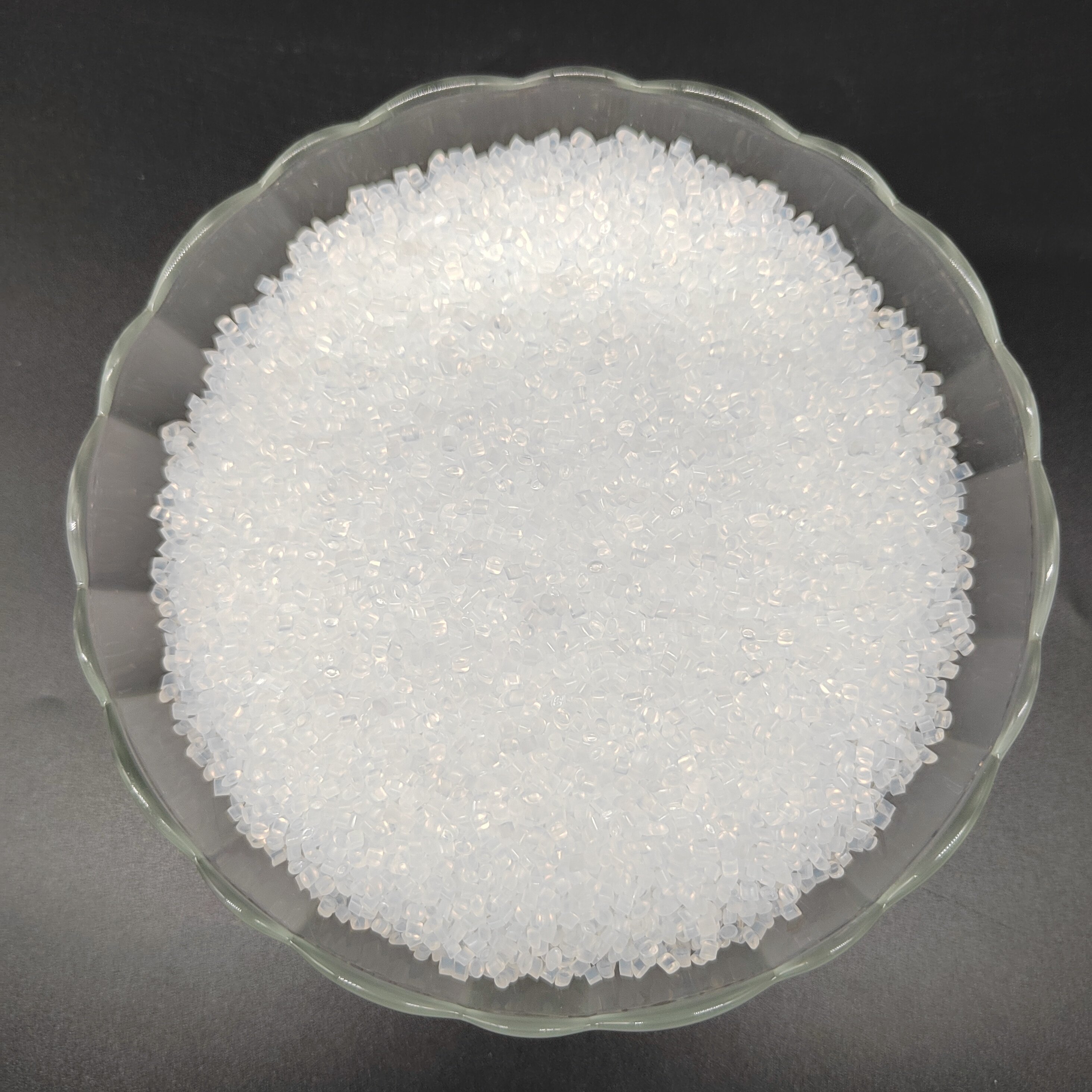
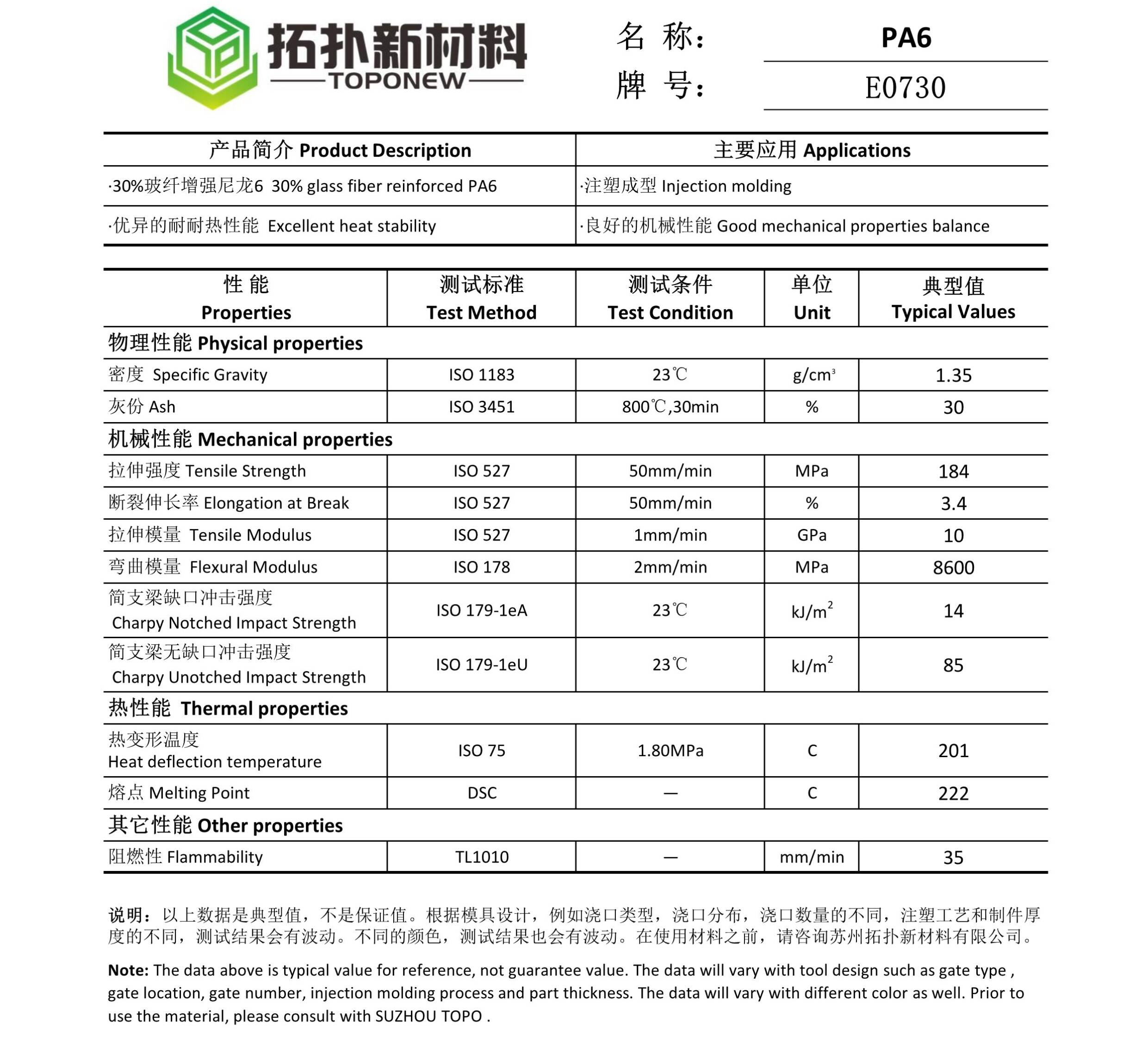
PA6 GF30 E0730
Glass Filled: 30%
(Custom materials available according to your Technical Data Sheet)
- Product Details
-
Download

Customizable Materials Available:
- Color (Customization of plastic pellet color according to your requirements.)
- Flame retardant grade (Let us know which flame retardant level you need: 0.8mm-3.0mm HB, V0, V1, V2, 5VA, 5VB)
- Glass fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- Carbon fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- UV resistance property (Tell us the application scenarios or UV resistance level of the materials )
- Other materials can also be customized ( Just need to provide your Technical Data Sheet. )
Technical Data Sheet of PA6 GF30 E0730
Nylon 6/ PA6 Plastic Particle Granule With 30%Gf
PA6 glass-filled granules are a type of engineering thermoplastic material that combines polyamide 6 (PA6) resin with glass fibers. The addition of glass fibers enhances the properties of PA6, resulting in a composite material with improved strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability.
Polyamide Nylon 6 (PA6) is a highly versatile and widely used thermoplastic belonging to the family of engineering design plastics. At TOPONEW, we are proud suppliers of high-quality PA6 plastic pellets with excellent performance properties. PA6, with its unique polyamide 6 structure, offers an exceptional combination of strength, toughness, and chemical resistance. Density of nylon 6 30 gf is around 1.35g/cm3. Its superior properties make it ideal for a wide range of applications in various industries. With our stringent manufacturing processes and adherence to strict quality standards, our PA6 plastic pellets meet the highest nylon 6 specifications, ensuring enhanced durability and reliability for your engineering design projects.
Properties of PA6 Glass-Filled Granules:
PA6 glass-filled granules offer several enhanced properties compared to unfilled PA6:
Increased strength: The incorporation of glass fibers improves the tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance of PA6, making it suitable for applications requiring high mechanical performance.
Enhanced rigidity: Glass fibers provide stiffness and dimensional stability to the PA6 matrix, improving its resistance to deformation under load.
Improved heat resistance: The presence of glass fibers helps to increase the heat deflection temperature of PA6, allowing it to withstand higher temperatures without deformation.
Reduced shrinkage: Glass fibers assist in reducing the shrinkage and warpage of the material during cooling, enhancing the dimensional accuracy of molded parts.
Lowered coefficient of thermal expansion: The addition of glass fibers reduces the coefficient of thermal expansion, making PA6 glass-filled granules less prone to size variation with temperature changes.
Applications of PA6 Glass-Filled Granules:
Due to their enhanced properties, PA6 glass-filled granules are commonly used in various demanding applications, including:
Automotive Industry: PA6 glass-filled granules are employed in the manufacturing of automotive components such as engine covers, intake manifolds, gears, and structural parts where high strength and heat resistance are required.
Electrical and Electronics: They find application in electrical connectors, housings, and switches, where their enhanced strength and dimensional stability are crucial.
Industrial Equipment: PA6 glass-filled granules are utilized in the production of machinery components, bearings, and gears that require high strength and wear resistance.
Sporting Goods: They are used in the manufacturing of sports equipment such as racquets, protective gear, and parts of bicycles and motorcycles, benefiting from their improved strength and rigidity.
In summary, PA6 glass-filled granules combine the properties of polyamide 6 with glass fibers to create a composite material with enhanced strength, rigidity, and heat resistance. Their applications span various industries, including automotive, electrical, electronics, industrial, and sporting goods, where superior mechanical performance and dimensional stability are required.
Q & A
1.Nylon 6 and 66 difference
Nylon 6 and nylon 66 are two different types of polyamides (nylon) with slight variations in their chemical structure and properties. Here are the main differences between nylon 6 and nylon 66:
-
Monomers: Nylon 6 is derived from the monomer called caprolactam, while nylon 66 is synthesized from the combination of adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine.
-
Structure: Nylon 6 has a slightly different chemical structure compared to nylon 66. Nylon 6 consists of a single amine group (-NH-) and a single acid group (-COOH) in each repeating unit. In contrast, nylon 66 has two amine groups and two acid groups in each repeating unit.
-
Melting Point: Nylon 6 has a lower melting point than nylon 66. Nylon 6 typically melts around 215-220°C, while nylon 66 has a higher melting point around 250-265°C. This difference in melting point can affect the processing and molding characteristics of the two materials.
-
Properties: Nylon 6 and nylon 66 exhibit slightly different properties. Nylon 66 is known for its higher tensile strength, stiffness, and heat resistance compared to nylon 6. On the other hand, nylon 6 has better impact resistance and flexibility.
-
Applications: Due to their different properties, nylon 6 and nylon 66 find applications in various industries. Nylon 6 is commonly used in textile fibers, carpeting, and engineering plastics, while nylon 66 is often utilized in automotive components, electrical connectors, and industrial applications where higher strength and heat resistance are required.
It's important to note that these are just some of the general differences between nylon 6 and nylon 66, and there may be specific variations or modifications based on the manufacturing process or desired properties for particular applications.
Download
-
PA6GF30.pdf
Download PA6GF30.pdf










