Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Please enter the email address you’d like your password reset information sent to.
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
Reset account password
For the account
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Reset success
Your password was reset. You can log in using your new password.
Login

Offer Technical Support and Customized Solutions
The company is committed to creating new and improved plastic materials to meet the evolving demands of the market.

Is flame retardant equal to non-flammable?
2024-03-06 14:13:20
https://youtube.com/shorts/IPNmjNpehDE?si=iHjw4AIX2uzFn0sy
Introduction:
Is flame retardant equal to non-flammable?
Flame retardant materials can reduce the speed of flame spread in a fire, but it does not mean the material will not burn completely. We usually use the UL94 standard to measure the flame retardancy of materials.
In the realm of material science, ensuring safety and reliability is paramount, especially when it comes to materials' behavior in the event of a fire. Among the various standards available for evaluating flame retardancy, UL94 stands out as one of the most widely recognized and utilized benchmarks. Developed by Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (UL), a leading authority in safety testing, the UL94 standard provides crucial insights into a material's ability to resist combustion and extinguish flames. This blog aims to delve into the intricacies of UL94 flame retardant testing standards, shedding light on its significance and methodologies.
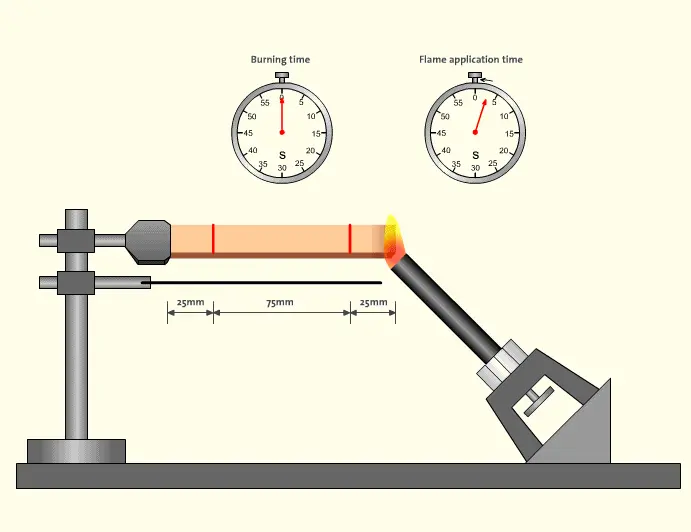
HB is the lowest flame retardant rating in the UL 94 standard. The test method is to horizontally clamp one end of the test piece at an angle of 45±2 degrees, take an iron mesh, and horizontally fix it 10±1mm below the test piece. The burner (flame height is about 20mm) is set at an angle of 45 degrees, moved to the other end of the test piece and contacts the sample 6mm, and timing starts after 30±1 seconds. When the test piece burns to the 25mm mark, start another timer. If it burns to the 25 mm mark within 30±1 seconds, start another timer and move the burner away.
UL 94 V test
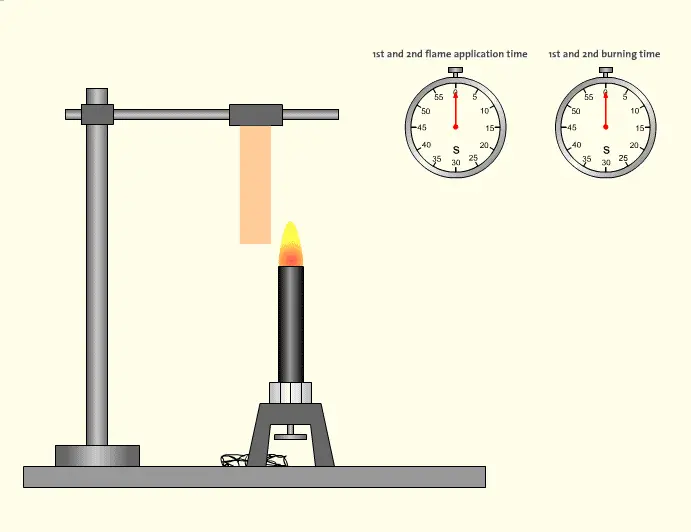
The UL 94-V test is completely different from the HB test. Compared with the HB test, the material has higher flame retardancy. After igniting the sample at the center below the sample with a burner (flame height is about 20mm) for 10±0.5 seconds, move the burner away from the sample at a speed of 300mm/s, at least 150mm away from the sample, and record the first self-ignition time. After the self-ignition stops, immediately perform the second burning. After burning for 10±0.5 seconds, move the burner away and record the second self-ignition time and the red-hot time after the flame is extinguished.
UL 94-5V test
The UL 94-5V test is stricter than the UL 94-V test, and the test is divided into two stages.
First, the strip-shaped sample is placed vertically for combustion testing, and after passing, a flat plate test is conducted.
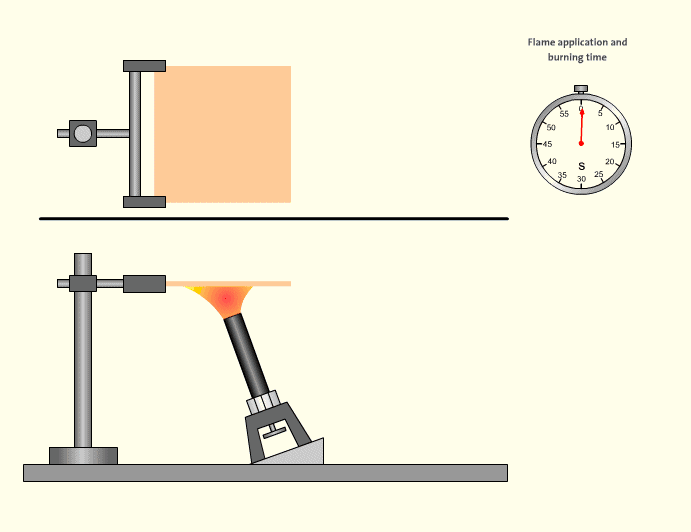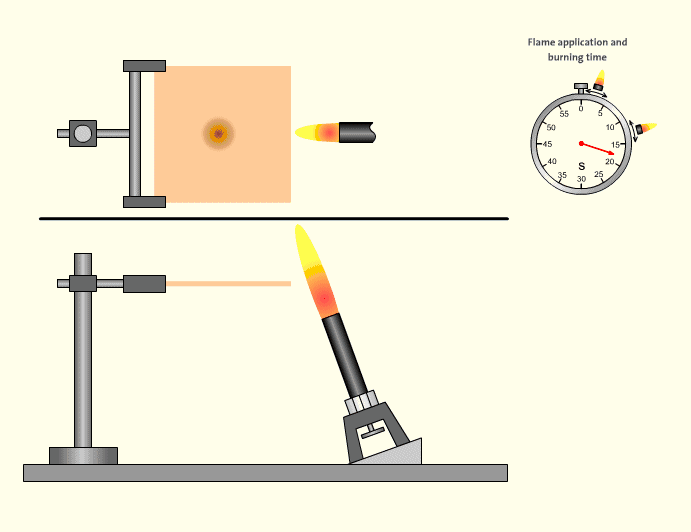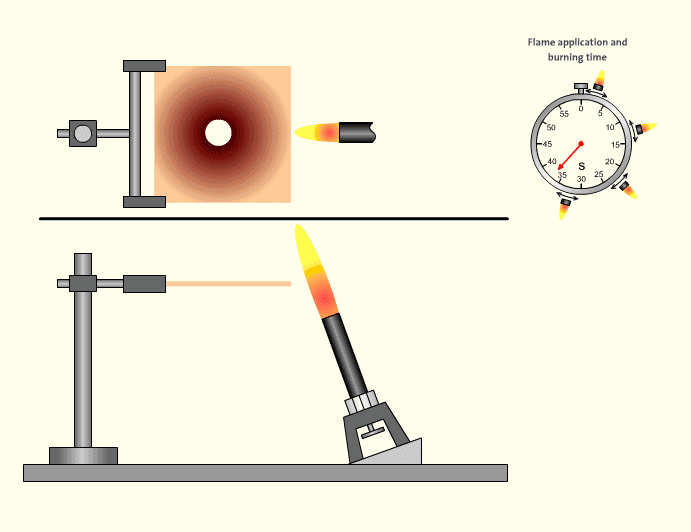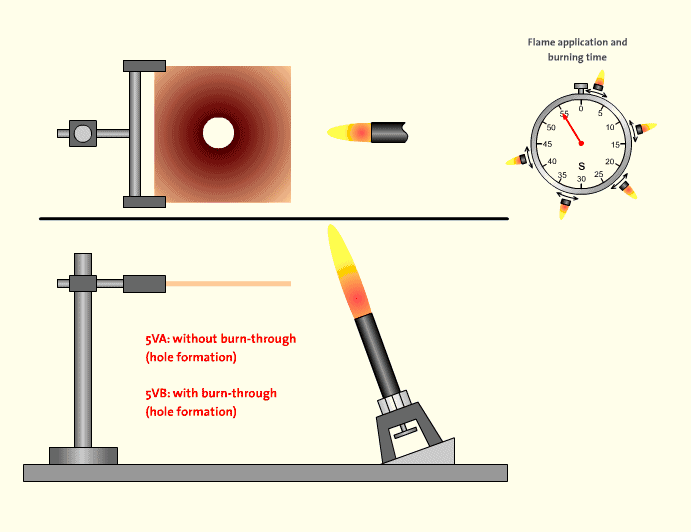
Phase 1: Fix the test piece horizontally with fixtures or jigs, and move the burner to an angle of 20±5 degrees with the horizontal. The tip of the inner flame contacts the bottom center point of the sample and burns for 5±0.5 seconds, then move the burner away for 5±0.5 seconds, repeat this action five times, and observe and record whether the test piece has holes or damage after the fifth burning.
Phase 2: Keep the burner (flame height is about 125mm) moving to the side of the test piece at an angle of 20±5 degrees, so that the tip of the inner flame (height 40mm±2mm) contacts one side of the bottom end of the sample, burn for 5±0.5 seconds, then move the burner away for 5±0.5 seconds, repeat this action five times, and record the self-ignition time and the red-hot time after the flame is extinguished after the fifth burning.
UL 94-5V Burning Judgment Criteria
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while flame retardant materials play a crucial role in fire safety, it's essential to understand that they don't render materials completely non-flammable. The UL94 standard provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating flame retardancy, ensuring that materials meet stringent safety criteria. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can enhance the fire safety of their products, fostering consumer confidence and trust.
Introduction:
Is flame retardant equal to non-flammable?
Flame retardant materials can reduce the speed of flame spread in a fire, but it does not mean the material will not burn completely. We usually use the UL94 standard to measure the flame retardancy of materials.
In the realm of material science, ensuring safety and reliability is paramount, especially when it comes to materials' behavior in the event of a fire. Among the various standards available for evaluating flame retardancy, UL94 stands out as one of the most widely recognized and utilized benchmarks. Developed by Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (UL), a leading authority in safety testing, the UL94 standard provides crucial insights into a material's ability to resist combustion and extinguish flames. This blog aims to delve into the intricacies of UL94 flame retardant testing standards, shedding light on its significance and methodologies.
Types of UL94 Flame Retardant Ratings and Testing Procedures and Criteria:
UL 94-HB testHB is the lowest flame retardant rating in the UL 94 standard. The test method is to horizontally clamp one end of the test piece at an angle of 45±2 degrees, take an iron mesh, and horizontally fix it 10±1mm below the test piece. The burner (flame height is about 20mm) is set at an angle of 45 degrees, moved to the other end of the test piece and contacts the sample 6mm, and timing starts after 30±1 seconds. When the test piece burns to the 25mm mark, start another timer. If it burns to the 25 mm mark within 30±1 seconds, start another timer and move the burner away.

UL 94 V test
The UL 94-V test is completely different from the HB test. Compared with the HB test, the material has higher flame retardancy. After igniting the sample at the center below the sample with a burner (flame height is about 20mm) for 10±0.5 seconds, move the burner away from the sample at a speed of 300mm/s, at least 150mm away from the sample, and record the first self-ignition time. After the self-ignition stops, immediately perform the second burning. After burning for 10±0.5 seconds, move the burner away and record the second self-ignition time and the red-hot time after the flame is extinguished.

UL 94-5V test
The UL 94-5V test is stricter than the UL 94-V test, and the test is divided into two stages.
First, the strip-shaped sample is placed vertically for combustion testing, and after passing, a flat plate test is conducted.
Phase 1: Fix the test piece horizontally with fixtures or jigs, and move the burner to an angle of 20±5 degrees with the horizontal. The tip of the inner flame contacts the bottom center point of the sample and burns for 5±0.5 seconds, then move the burner away for 5±0.5 seconds, repeat this action five times, and observe and record whether the test piece has holes or damage after the fifth burning.
Phase 2: Keep the burner (flame height is about 125mm) moving to the side of the test piece at an angle of 20±5 degrees, so that the tip of the inner flame (height 40mm±2mm) contacts one side of the bottom end of the sample, burn for 5±0.5 seconds, then move the burner away for 5±0.5 seconds, repeat this action five times, and record the self-ignition time and the red-hot time after the flame is extinguished after the fifth burning.

UL 94 Flame Retardant Rating Determination Standard
UL 94-HB Burning Judgment Criteria
| Judgment conditions | Burning Rate | Flammability rating |
| Sample thickness 3-13mm | ≤40mm/min | HB |
| Sample thickness <3mm | ≤75mm/min | HB |
| The flame goes out before the marking line (25||100mm) | =0mm/min | HB |
UL 94-V Burning Judgment Criteria
UL 94-5V Burning Judgment Criteria
| Judgment conditions | 5VA | 5VB |
| Flaming plus glowing time after 5 flame applications for any given sample (s) | ≤60 | ≤60 |
| Droplets ignite cotton wool | no | no |
|
Sample holed (<3mm) |
no | yes |
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while flame retardant materials play a crucial role in fire safety, it's essential to understand that they don't render materials completely non-flammable. The UL94 standard provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating flame retardancy, ensuring that materials meet stringent safety criteria. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can enhance the fire safety of their products, fostering consumer confidence and trust.
Contact us

