Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

Offer Technical Support and Customized Solutions
The company is committed to creating new and improved plastic materials to meet the evolving demands of the market.

The Future of Halogen-free Flame Retardant PA6, PA66
In recent years, with the increasing global environmental awareness, halogen-free flame retardant materials have been receiving more and more attention, especially high-performance halogen-free flame retardant nylon materials are becoming popular.
However, unmodified nylon has poor flame retardant properties and is a flammable material, often leading to dripping during combustion, making it prone to causing fires during use. Therefore, flame retardant modification of nylon has become a topic of common concern and research in both the academic and industrial fields. Scientists later introduced flame retardants into nylon, changing its flame retardant properties, making nylon more versatile.
The term "halogen-free" in halogen-free flame retardant nylon refers to the type of flame retardant used. Flame retardants are classified into halogen-containing and halogen-free types. In the early stages of modification, flame retardant modifications were mainly done using halogen-containing flame retardants, such as bromine-based flame retardants. However, since the dioxin issue emerged in 1986, bromine-based flame retardants have faced significant environmental pressure, sparking global controversies over their usage.
Halogen-free flame retardants have resolved this issue. The most widely used halogen-free flame retardants in nylon are red phosphorus and melamine cyanurate salts. Red phosphorus has high flame retardant efficiency and can improve the arc resistance of products, but its limitations in terms of storage and color greatly restrict its application in nylon, usually only used for nylon 6. Another halogen-free flame retardant used in nylon is melamine cyanurate salts, mainly melamine cyanurate and phosphate salts. They have good flame retardant efficiency but poor heat stability, and their moisture absorption can result in poor electrical properties of the products in humid environments.
Halogen-free flame retardant nylon has very low or no halogen elements of bromine and chlorine among the added flame retardants. Products of halogen-free flame retardant nylon exhibit outstanding flame retardant performance, reaching UL94V0 level, with low emissions, non-dripping, high electrical performance, excellent heat resistance, high CTI value, good electrical properties, high impact strength, environmentally friendly, and eco-friendly. They are suitable for use in electrical connectors. By adding bromine-based flame retardants or halogen-free flame retardants that comply with European RoHS standards to the material, the flame retardant performance of composite materials can be enhanced. This pelletized nylon can withstand processing temperatures of up to 260°C.
Sometimes in the process of using halogen-free flame retardant nylon granules, we encounter markings such as UL94V-0, UL94V-2, and so on. The combustibility UL94 rating is the most widely used combustibility performance standard for plastic materials.
UL94V0 level meets 5 standards and requirements:
1.No sample continues to burn for more than 10 seconds after the flame is removed from the test;
2.The total burning time with a flaming time after igniting each of the five sets of samples 10 times should not exceed 50 seconds;
3.No sample continues to burn onto the holder;
4.No sample drips and ignites cotton 12 inches below;
5.No sample continues to glow for more than 30 seconds after the flame is removed for a second time.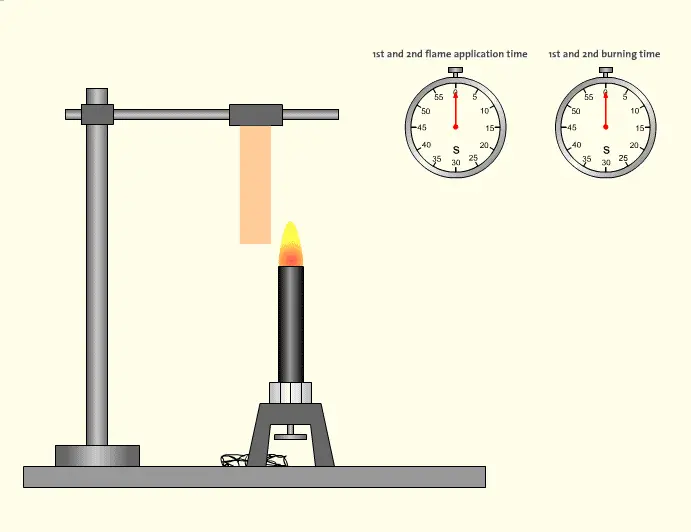
Such standards are crucial in preventing fires.
With the increasingly widespread application of nylon engineering plastics and the development of a variety of flame retardants, as well as the ongoing deepening of flame retardant technology research and development, flame retardant nylon is expected to develop in the following four directions in the coming decades:
Compound flame retardant technology. Many international flame retardant manufacturers are developing new synergistic systems by blending multiple flame retardants to reduce the amount of flame retardants required and enhance flame retardant performance, thereby reducing the price of flame retardant materials and mitigating the loss of physical properties.
Halogen-free, low-toxic halogen-free formulations. Many countries have already prohibited or restricted the use of halogen-containing flame retardants, favoring phosphorus, nitrogen-based flame retardants, and inorganic flame retardants.
Multifunctional applications. In some industries, in addition to requiring flame retardant properties in nylon, there is also a demand for additional features such as thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and static resistance, necessitating the addition of other additives to meet user requirements.
Balancing cost and performance. Developing efficient flame retardant systems to reduce the impact of flame retardants on material physical properties while also reducing pollution and lowering costs.

